化石燃料依赖
Search documents
你“吃下”了多少化石燃料?
Hu Xiu· 2025-10-16 11:39
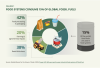
Core Insights - The food system is heavily reliant on fossil fuels, consuming at least 15% of the world's fossil fuels and 40% of petrochemical products, which are crucial derivatives of fossil fuels [1][2][3] Group 1: Fossil Fuel Consumption in Food Systems - Over 42% of fossil fuel consumption in the food system occurs during food processing and packaging, while nearly 38% is used in retail and kitchen cooking [3][5] - The food system consumes 40% of global petrochemical products, with 34% used for fertilizer production, highlighting the significant role of fossil fuels in agricultural inputs [5][8] Group 2: Nitrogen Fertilizer and Environmental Impact - Nitrogen fertilizer production is a major contributor to fossil fuel consumption, with its usage increasing by 800% since 1961, particularly in high-income countries [9][10] - The nitrogen fertilizer supply chain contributes to 2% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with 60% of emissions arising from the application of fertilizers in the field [9][10] Group 3: Energy Use in Food Processing - The food processing sector is energy-intensive, with 60% to 70% of its total energy consumption coming from heat generated by burning fossil fuels [19][23] - Ultra-processed foods, which are heavily reliant on fossil fuels, account for a significant portion of caloric intake in both high-income and low-income countries [19][23] Group 4: Plastic Use and Waste in Food Systems - The food system is a major consumer of plastics, with 74% of petrochemical products used in plastic and fertilizer production, and Asia being a significant contributor to global plastic packaging [23][24] - Less than 10% of plastics are recycled globally, with food packaging being one of the most challenging types to recycle due to contamination [25][26] Group 5: Recommendations for Reducing Fossil Fuel Dependency - The report suggests eight actions to reduce the food system's reliance on fossil fuels, including promoting ecological agriculture, reducing plastic production, and curbing ultra-processed food consumption [30]