恒星磁活动
Search documents
科学家观测到太阳以外的恒星爆发
Xin Hua She· 2025-11-17 12:29
Core Insights - Researchers observed an explosion from a red dwarf star located over 130 light-years away, marking a significant discovery in stellar activity [1][2] - The observation was made using the Low-Frequency Array (LOFAR) radio telescope, revealing a phenomenon similar to solar coronal mass ejections, which are crucial for understanding space weather [1] - This finding opens new avenues for applying space meteorology to the study of other stellar systems, particularly in understanding how stellar magnetic activity affects the habitability of surrounding planets [1][2] Group 1 - The red dwarf star is significantly dimmer, cooler, and smaller than the Sun, and the observed explosion is a rare event that had not been previously documented outside of the Sun [1] - The research indicates that while many known planets in the Milky Way orbit red dwarf stars, frequent explosions from these stars could strip away the atmospheres of these planets, rendering them uninhabitable despite being in the habitable zone [2] - The results of this research have been published in the journal Nature, contributing to the scientific community's understanding of stellar phenomena [3]
中国天眼,有新发现!
券商中国· 2025-10-19 23:37
Core Viewpoint - The research team from Peking University has detected a new type of millisecond radio burst originating from the magnetic field of stellar sunspot regions using the "China Sky Eye" (FAST), filling a gap in understanding small-scale magnetic fields of exoplanetary stars and significantly contributing to the study of space weather beyond the solar system [1][2]. Group 1 - The solar magnetic field drives solar activity, which typically originates from localized strong magnetic field regions such as sunspots [1]. - Similar magnetic activity phenomena exist on other late-type stars, with some stars (like active M-type stars) exhibiting more intense and frequent magnetic activities than the Sun, significantly affecting the habitability of nearby planets [1]. - Traditional methods for measuring stellar magnetic fields have primarily provided large-scale global magnetic field information, lacking the ability to discern small-scale magnetic structures in stellar sunspot regions [1]. Group 2 - The high sensitivity radio observations from "China Sky Eye" offer a new complementary approach to optical methods for detecting and studying sunspots [1]. - By detecting radio signals emitted from the localized magnetic field structures above stellar sunspots, the research team can constrain the size of the sunspots and understand the strength and structure of the coronal magnetic field above them, accurately characterizing the properties of stellar sunspots [1]. - The research team is also utilizing FAST to explore young solar-type stars, brown dwarfs, and stellar-planet interaction processes, which will further expand understanding of stellar magnetic activities and their driven exoplanetary space weather phenomena, providing important insights for the search for habitable exoplanets [2].
“中国天眼”,捕获新的毫秒级射电暴
财联社· 2025-10-19 02:33
Core Insights - The research team from Peking University's School of Earth and Space Sciences has detected a new type of millisecond radio burst originating from the magnetic field of stellar sunspot regions using the "Chinese Sky Eye" (FAST) [1][3] - This discovery fills a gap in understanding the small-scale magnetic fields of stars outside the solar system and is significant for advancing research on space weather beyond the solar system [1][3] Group 1 - The solar magnetic field drives solar activity, which typically originates from localized strong magnetic field regions such as sunspots [3] - Similar magnetic activity phenomena exist on other late-type stars, with some stars (like active M-type stars) exhibiting more intense and frequent magnetic activities, significantly affecting the habitability of nearby planets [3] - Measuring small-scale magnetic fields of stars is crucial for exploring the origins of stellar magnetic activity and assessing potential space weather effects [3] Group 2 - Traditional methods for measuring stellar magnetic fields, such as Zeeman Doppler imaging, primarily provide information on the global large-scale magnetic fields of stars, lacking the ability to discern small-scale magnetic structures in sunspot regions [3] - The high sensitivity radio observations from the "Chinese Sky Eye" offer a new complementary approach to optical methods for detecting and studying sunspots [3] - The research team is also utilizing FAST observations to explore young solar-type stars, brown dwarfs, and stellar-planet interaction processes, which will further enhance understanding of stellar magnetic activities and their driven exoplanetary space weather phenomena [3]
中国天眼,有新发现!
Qi Lu Wan Bao· 2025-10-18 08:25
Core Insights - A research team led by Professor Tian Hui from Peking University has successfully detected millisecond-level radio burst signals from stellar sunspot regions using the FAST (Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope) [2] - This discovery provides a new observational method for directly measuring the small-scale magnetic fields of stars and revealing the origins of stellar magnetic activity [2] Group 1: Research Findings - The detection of radio signals indicates that magnetic activity in stellar sunspot regions can accelerate electrons to extremely high energies, which then produce unique radio emissions as they spiral in the magnetic field [2] - Capturing these radio signals allows for direct analysis of the small-scale magnetic field structures on stellar surfaces, offering insights into the origins of stellar magnetic activity and the complex magnetic field structures of stars [2] Group 2: Technological Advancements - The success of this research is attributed to the high sensitivity and high resolution of the FAST telescope, which has improved the time resolution of stellar radio observations to the "sub-millisecond" level [2] - This advancement enables the capture of subtle variations in stellar radio emissions, making FAST one of the few devices in the world capable of such detailed observations [2]
首次捕获!这一大国重器有重要发现
证券时报· 2025-10-18 07:24
Core Viewpoint - The research team led by Professor Tian Hui from Peking University has successfully detected millisecond-level radio burst signals from stellar sunspot regions using the FAST telescope, providing a new observational method for studying stellar magnetic activity and its origins [2]. Group 1: Research Findings - The detection of radio signals indicates that magnetic activity in stellar sunspot regions can accelerate electrons to high energies, which then produce unique radio emissions as they spiral in the magnetic field [2]. - This breakthrough allows for direct analysis of the small-scale magnetic field structure on stellar surfaces, enhancing the understanding of complex stellar magnetic fields [2]. Group 2: Technological Advancements - The success of this research is attributed to the high sensitivity and resolution of the FAST telescope, which has improved the time resolution of stellar radio observations to the "sub-millisecond" level, enabling the capture of minute variations in stellar radio emissions [3]. - Currently, there are very few devices worldwide that can match the capabilities of FAST in this regard [3].
首次捕获!这一大国重器有重要发现
Ke Ji Ri Bao· 2025-10-18 06:07
Core Insights - A research team led by Professor Tian Hui from Peking University has successfully detected millisecond-level radio burst signals from stellar sunspot regions using the FAST telescope, providing a new observational method for studying stellar magnetic activity and its origins [1] Group 1: Research Findings - The detection of radio signals indicates that magnetic activity in stellar sunspot regions can accelerate electrons to extremely high energies, which then produce unique radio emissions as they spiral in the magnetic field [1] - This breakthrough allows for direct analysis of the small-scale magnetic field structure on stellar surfaces, enhancing the understanding of complex stellar magnetic fields [1] Group 2: Technological Advancements - The success of this research is attributed to the high sensitivity and resolution of the FAST telescope, which has improved the time resolution of stellar radio observations to the sub-millisecond level, capturing minute variations in stellar radio emissions [1] - Currently, there are very few devices worldwide that can match the capabilities of FAST in this regard [1]
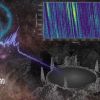
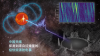
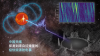
“中国天眼”立新功 首次捕获恒星黑子区射电暴信号
Ke Ji Ri Bao· 2025-10-18 03:24
Core Viewpoint - The research team led by Professor Tian Hui from Peking University has successfully detected millisecond-level radio burst signals from the sunspot region of a star using the FAST telescope, providing a new observational method for studying stellar magnetic activity and its origins [1][4]. Group 1: Stellar Magnetic Activity - Sunspots are localized regions of strong magnetic fields on the surface of stars, and their magnetic activity can disrupt the space environment around Earth, affecting satellite operations and communication systems [4]. - Traditional methods for measuring stellar magnetic fields have struggled to capture small-scale magnetic structures, often only providing information on large-scale magnetic fields [4]. - The detection of a unique radio burst from the active red dwarf star AD Leo, with a frequency drift rate of approximately 8 GHz per second, indicates that the radiation source is from a high magnetic field region very close to the star's surface [4][5]. Group 2: Implications of the Discovery - The findings suggest that magnetic activity in stellar sunspot regions can accelerate electrons to high energies, producing unique radio emissions that allow for direct analysis of small-scale magnetic field structures on stars [5]. - The success of this research is attributed to the high sensitivity and resolution of the FAST telescope, which has improved time resolution to the sub-millisecond level, enabling the capture of minute variations in stellar radio emissions [5]. - This research opens new avenues for studying magnetic activity in late-type stars and exploring interactions between stars and planets, potentially aiding in the search for habitable exoplanets [5].