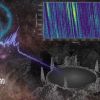
中国天眼(500米口径球面射电望远镜FAST)
Search documents
“中国天眼”揭示快速射电暴双星起源关键证据 极目星河深处 求索未解之谜(科技自立自强)
Ren Min Ri Bao· 2026-01-18 22:05
Core Viewpoint - The research team led by the Chinese Academy of Sciences has found key evidence regarding the origin of fast radio bursts (FRBs), suggesting they may originate from binary star systems, as reported in the journal "Science" [1][2]. Group 1: Fast Radio Bursts Research - Fast radio bursts are mysterious cosmic phenomena that release energy equivalent to the total radiation of the Sun over a week in just milliseconds [2]. - The team monitored the repeating fast radio burst FRB 20220529 for over two years, utilizing the high sensitivity of the "Chinese Sky Eye" [2][3]. - A significant observation was made when the Faraday rotation measure of FRB 20220529 surged to 20 times its normal level before returning to typical fluctuations, marking a first in recorded FRB studies [2][3]. Group 2: Scientific Contributions of the "Chinese Sky Eye" - Since its operation began in 2020, the "Chinese Sky Eye" has maintained high efficiency, with over 5400 hours of observation and more than 17.5 petabytes of new scientific data generated in the last complete observation year [4]. - The telescope has produced groundbreaking results in various fields, including the detection of gravitational waves, pulsar searches, and studies of neutral hydrogen [5]. - The "Chinese Sky Eye" has also improved radar imaging resolution of the Moon from kilometers to 10 meters, aiding geological studies and resource exploration [6]. Group 3: Future Developments and Upgrades - The "Chinese Sky Eye" is advancing its upgrade plans to become a "super probe" of the universe, with ongoing research to replace imported components with domestically produced alternatives [7][8]. - By 2025, two core array antennas will be completed, enhancing observational capabilities and addressing long-standing astrophysical questions [8].
中国天眼,有新发现!
券商中国· 2025-10-19 23:37
Core Viewpoint - The research team from Peking University has detected a new type of millisecond radio burst originating from the magnetic field of stellar sunspot regions using the "China Sky Eye" (FAST), filling a gap in understanding small-scale magnetic fields of exoplanetary stars and significantly contributing to the study of space weather beyond the solar system [1][2]. Group 1 - The solar magnetic field drives solar activity, which typically originates from localized strong magnetic field regions such as sunspots [1]. - Similar magnetic activity phenomena exist on other late-type stars, with some stars (like active M-type stars) exhibiting more intense and frequent magnetic activities than the Sun, significantly affecting the habitability of nearby planets [1]. - Traditional methods for measuring stellar magnetic fields have primarily provided large-scale global magnetic field information, lacking the ability to discern small-scale magnetic structures in stellar sunspot regions [1]. Group 2 - The high sensitivity radio observations from "China Sky Eye" offer a new complementary approach to optical methods for detecting and studying sunspots [1]. - By detecting radio signals emitted from the localized magnetic field structures above stellar sunspots, the research team can constrain the size of the sunspots and understand the strength and structure of the coronal magnetic field above them, accurately characterizing the properties of stellar sunspots [1]. - The research team is also utilizing FAST to explore young solar-type stars, brown dwarfs, and stellar-planet interaction processes, which will further expand understanding of stellar magnetic activities and their driven exoplanetary space weather phenomena, providing important insights for the search for habitable exoplanets [2].
全球首台、世界最大!上周末 大国工程捷报频传
Yang Shi Xin Wen· 2025-10-19 23:16
Group 1 - The world's first mid-infrared solar magnetic field observation system (AIMS telescope) has been officially launched, marking a significant advancement in China's astronomical instruments and filling an international gap in mid-infrared solar magnetic field observation [2] - The "China Sky Eye" (FAST) has detected a new type of millisecond radio burst originating from the magnetic field of stellar sunspots, contributing to the understanding of small-scale magnetic fields beyond the solar system [3] - The successful installation of the first steel beam for the Shitou Yangtze River Bridge of the Chongqing-Wanzhou High-speed Railway marks a critical construction milestone, with the bridge expected to set four world records upon completion [4][8] Group 2 - The successful damming of the Changbo Hydropower Station on the Jinsha River represents a key breakthrough for one of China's largest hydropower projects, with the station projected to generate over 4.3 billion kilowatt-hours of clean energy annually, significantly reducing coal consumption and carbon emissions [6]
“中国天眼”,捕获新的毫秒级射电暴
财联社· 2025-10-19 02:33
Core Insights - The research team from Peking University's School of Earth and Space Sciences has detected a new type of millisecond radio burst originating from the magnetic field of stellar sunspot regions using the "Chinese Sky Eye" (FAST) [1][3] - This discovery fills a gap in understanding the small-scale magnetic fields of stars outside the solar system and is significant for advancing research on space weather beyond the solar system [1][3] Group 1 - The solar magnetic field drives solar activity, which typically originates from localized strong magnetic field regions such as sunspots [3] - Similar magnetic activity phenomena exist on other late-type stars, with some stars (like active M-type stars) exhibiting more intense and frequent magnetic activities, significantly affecting the habitability of nearby planets [3] - Measuring small-scale magnetic fields of stars is crucial for exploring the origins of stellar magnetic activity and assessing potential space weather effects [3] Group 2 - Traditional methods for measuring stellar magnetic fields, such as Zeeman Doppler imaging, primarily provide information on the global large-scale magnetic fields of stars, lacking the ability to discern small-scale magnetic structures in sunspot regions [3] - The high sensitivity radio observations from the "Chinese Sky Eye" offer a new complementary approach to optical methods for detecting and studying sunspots [3] - The research team is also utilizing FAST observations to explore young solar-type stars, brown dwarfs, and stellar-planet interaction processes, which will further enhance understanding of stellar magnetic activities and their driven exoplanetary space weather phenomena [3]
“中国天眼”首次捕获恒星黑子区射电暴信号
Yang Shi Xin Wen· 2025-10-18 15:08
Core Insights - A research team from Peking University's School of Earth and Space Sciences has detected a new type of millisecond radio burst originating from the magnetic field of stellar sunspot regions using the "China Sky Eye" (FAST) [1] - This discovery fills a gap in understanding the small-scale magnetic fields of stars outside the solar system and is significant for advancing research on space weather beyond the solar system [1] - The findings were published in the international academic journal "Science Advances" [1]