影子银行
Search documents
美国制裁伊朗最高国家安全委员会秘书及影子银行网络
Xin Lang Cai Jing· 2026-01-15 16:20
Core Viewpoint - The U.S. Department of the Treasury has imposed sanctions on Ali Larijani, the Secretary of Iran's Supreme National Security Council, along with 18 individuals and entities linked to a shadow banking network [1] Group 1: Sanctions Details - The sanctioned entities include Crystal Gas and other companies associated with Iran [1] - The sanctions related to the shadow banking network are connected to previous sanctions against Iran's National Bank and Shahr Bank [1]
突发!2.4万亿资金,突然“消失”!黑天鹅来袭?
券商中国· 2025-12-18 23:29
Core Viewpoint - The article discusses the ongoing liquidity tightening in the global financial system, highlighting the actions of JPMorgan Chase in reallocating significant reserves to U.S. government bonds in anticipation of interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve [1][2]. Group 1: JPMorgan Chase's Actions - Since 2023, JPMorgan Chase has withdrawn nearly $350 billion from its Federal Reserve account, primarily investing in U.S. government bonds to secure higher yields before potential interest rate cuts [2][3]. - The bank's deposits at the Federal Reserve have decreased from $409 billion at the end of 2022 to approximately $63 billion by the third quarter of 2023, while its holdings of U.S. Treasury securities have increased from $231 billion to $450 billion during the same period [2][3]. - This significant withdrawal by JPMorgan Chase has offset the total cash withdrawals of over 4,000 other banks from the Federal Reserve, indicating a potential impact on overall financial system liquidity [3]. Group 2: Shadow Banking System Risks - The shadow banking system, valued at $63 trillion, is emerging as a potential source of instability in global financial markets, particularly under high interest rate conditions [4][5]. - Private credit markets, currently around $1.8 trillion, pose another risk, as a significant portion of this capital is committed to long-term or structured assets lacking active secondary markets, which could lead to liquidity gaps under pressure [5]. - Recent trends in the credit market, including rising yields and falling prices for high-yield bonds, reflect investor concerns regarding non-traditional financing models and high-leverage capital structures [5][6]. Group 3: Federal Reserve's Response - The Federal Reserve has initiated a Reserve Management Purchase (RMP) program, purchasing $40 billion in short-term government bonds monthly to provide additional liquidity to the market, indicating a balancing act between inflation control and financial stability [5][6]. - Historical precedents show that liquidity strains in the shadow banking sector often precede broader financial market pressures, as seen during the 2008 financial crisis and the 2020 pandemic [6].
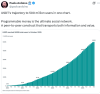
FSB报告:全球影子银行资产首破250万亿美元,监管真空引发系统性风险担忧
Zhi Tong Cai Jing· 2025-12-16 12:49
Group 1 - The global shadow banking system's assets have surpassed $250 trillion for the first time, raising concerns about systemic risks due to regulatory gaps [1] - As of the end of 2024, non-bank financial institutions' total assets reached a record $256.8 trillion, reflecting a year-on-year growth of 9.4% and accounting for 51% of total financial assets [1] - The fastest-growing segments within non-bank financial institutions include trust companies, hedge funds, money market funds, and other investment funds, all experiencing double-digit growth rates [1] Group 2 - The Financial Stability Board (FSB) expressed regret over the lack of relevant data regarding the growth of the private credit industry, which is under close scrutiny for potential signs of weakness [1] - FSB officials reported significant data gaps in private credit activities from eight major jurisdictions, with reported activities amounting to only $0.5 trillion, which is significantly lower than estimates derived from commercial data [2] - The FSB highlighted the absence of a global standard definition for private credit, complicating the identification of private credit entities in statistical and regulatory reports [2]
250万亿美元!影子银行规模突破250万亿美元大关
Xin Lang Cai Jing· 2025-12-16 09:26
Core Insights - The global asset size of the shadow banking system has surpassed $250 trillion for the first time, raising concerns about systemic risks in less regulated areas of the financial system [1][3]. Group 1: Shadow Banking Growth - As of the end of 2024, the total assets of non-bank financial institutions, including hedge funds, insurance companies, and investment funds, reached a record $256.8 trillion, representing a year-on-year growth of 9.4% [1][3]. - Non-bank financial institutions now account for 51% of total financial assets, maintaining a level similar to that before the pandemic [1][3]. - The fastest-growing segments within non-bank financial institutions are trust companies, hedge funds, money market funds, and other investment funds, all experiencing double-digit growth rates [1][3]. Group 2: Banking Sector Comparison - In contrast, the banking sector's assets grew by only 4.7% during the same period [1][3]. Group 3: Private Credit Industry Concerns - The Financial Stability Board (FSB) expressed regret over the lack of data regarding the growth of the private credit industry, which is estimated to be in the trillions of dollars [1][3]. - Regulatory bodies are closely monitoring potential risks in the private credit sector, with warnings issued by high-profile bank executives, including Jamie Dimon of JPMorgan and Colm Kelleher of UBS [1][3]. Group 4: Data Collection Challenges - Officials reported significant discrepancies in the data collected from eight major jurisdictions, including Canada, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Japan, Switzerland, and Hong Kong, with reported private credit activities amounting to only $0.5 trillion [2][4]. - The FSB noted that not all participating jurisdictions could provide comprehensive data, with some only reporting partial industry data [2][4]. - There is currently a lack of global standard definitions for private credit and finance, complicating the identification of private credit entities in statistical and regulatory reports [2][4]. The FSB's work plan for 2026 includes addressing data gaps in private credit [2][4].
美股震荡似2008!英伟达循环交易推泡沫,影子银行融资风险扩大
Sou Hu Cai Jing· 2025-12-03 04:20
Group 1 - The article discusses concerns over Trump's tariff policies, suggesting they may lead to economic issues in the U.S. and undermine confidence in the dollar-based financial system globally [1][13] - The U.S. stock market is experiencing a rise, but underlying mechanisms appear "virtual," with companies like Nvidia inflating valuations through internal financing arrangements [3][5] - There is a growing risk associated with cryptocurrency, as traditional financial institutions are integrating it despite its volatility, which could lead to significant financial instability [7][19] Group 2 - The U.S. national debt has reached $38 trillion, which is 1.25 times the annual GDP, with interest payments nearing $1 trillion annually, diverting funds from public welfare [11][13] - Japan's debt situation is also alarming, with a debt-to-GDP ratio of 2.6, raising concerns about the sustainability of its financial practices [13][15] - The International Monetary Fund (IMF) reports a decline in the dollar's share of global foreign exchange reserves to its lowest in decades, indicating a potential shift away from dollar reliance in international trade [15][17] Group 3 - The article highlights that countries like Brazil and India are increasingly opting for local currencies in trade, reducing their dependence on the dollar, which could further erode the dollar's dominance [17][19] - The interconnectedness of global economies means that financial issues in the U.S. could have widespread repercussions, potentially leading to a re-evaluation of the existing financial system [19][21] - The article concludes that without addressing these accumulating risks, the consequences could be severe, affecting not just the U.S. but the global population [21]
最近怎么这么难?全球皆跌,A股从4000点掉下来,持续亏钱!
雪球· 2025-11-18 13:00
Group 1 - The article discusses the recent fluctuations in the stock market, particularly the Shanghai Composite Index reaching new highs before experiencing a downturn, causing panic among investors [3][31]. - The absence of the U.S. CPI data has led to market fears regarding the Federal Reserve's cautious approach, with concerns that interest rates may not be lowered in December [4][6]. - The article highlights that despite the lack of CPI data, the Federal Reserve has other data to consider, and the current economic situation in the U.S. is not as strong as it appears, masked by the tech boom [9][10]. Group 2 - There has been a significant increase in non-bank loans in the U.S., with $550 billion in new loans in the first ten months of the year, marking a 40% growth rate [18][19]. - Non-bank loans have surpassed the total of real estate, industrial, and consumer loans combined, indicating a shift in credit dynamics [19][21]. - The article outlines the main areas where non-bank loans are directed, including commercial real estate, residential mortgages, corporate credit, and consumer finance, driven by tighter bank regulations and the need for flexible financing [22][23]. Group 3 - The article notes a style shift in the market, with a general decline influenced by overseas factors, while certain sectors like finance and small-cap stocks have shown resilience [31][33]. - The Hong Kong stock market is more affected by overseas influences, and there have been recommendations to increase positions in insurance and Hong Kong dividend stocks during corrections [34][39]. - The article emphasizes that despite internal style rotations, the overall index is still on a slow upward trend, with the Shanghai Composite Index reaching new highs [43][44]. Group 4 - Recent economic data shows a decline in M1 and M2 growth rates, with M1 decreasing to 6.2% and M2 to 8.2%, indicating potential challenges in the stock market [53][59]. - Retail sales growth has slowed to 2.93%, suggesting a sluggish recovery in consumer spending, with restaurant revenues showing some improvement [62][66]. - Real estate investment has dropped by 14.7% year-on-year, indicating ongoing challenges in the sector, but the article suggests that funds from the real estate market may flow into the stock market [67][68]. Group 5 - The article mentions a rebound in soybean meal prices, with potential for further increases if supply issues arise towards the end of the year [69]. - It highlights the cyclical nature of the market, emphasizing that returns are not linear and that investors should be prepared for periods of volatility [71][73]. - The article advises against certain mindsets during bull markets, such as chasing highs or being overly sensitive to account fluctuations, suggesting a focus on long-term investment strategies [76][77].
超越2008年危机:全球影子银行超1.7万亿!普通投资者如何自保?
Sou Hu Cai Jing· 2025-10-28 18:50
Core Viewpoint - A $1.7 trillion "black box market" of private credit is expanding, posing risks potentially greater than those seen during the 2008 Lehman Brothers crisis [1][3]. Group 1: Market Overview - The private credit market is becoming a significant risk hub within the global financial system, characterized by a lack of transparency and regulatory oversight [3][10]. - The market has grown at an alarming rate, exceeding 20% annually, with a current size of approximately $1.6 trillion [7][9]. Group 2: Risk Factors - Rising interest rates are creating a lagging effect, with many companies facing interest burdens that have increased by over 200% due to floating rates [10][11]. - There is a liquidity illusion in the market, where credit products are rarely traded, leading to potential price drops of 40% or more during market stress [11]. - The devaluation of collateral, such as corporate equity or real estate, poses a significant risk, especially if combined with rising rates and liquidity issues [11]. Group 3: Systemic Risk Concerns - The concentration of risk is notable, with the top ten private credit managers controlling over 80% of the market, making the system vulnerable to a domino effect from any single institution's failure [11]. - Commercial banks have deepened their involvement in the private credit market, increasing systemic risk as highlighted by stress tests from the Federal Reserve [11]. - There is a lack of effective resolution mechanisms for shadow banking institutions, which could complicate responses to a potential crisis [11]. Group 4: Warning Signals - The spread on CCC-rated CLOs has widened significantly, indicating growing concerns about default risks [12]. - There has been a historical high in early withdrawals from U.S. retirement accounts, suggesting individuals may be preparing for economic downturns [12]. - Bankruptcy filings among U.S. companies have increased by 61% year-over-year, with many being significant borrowers in the private credit space [12].
今年利润预计150亿美元,利润率高达99%,用户数超5亿,估值5000亿美元!“稳定币老大”Tether“春风得意”
美股IPO· 2025-10-25 05:14
Core Insights - Tether is expected to achieve a profit close to $15 billion this year, driven by a remarkable profit margin of 99% and substantial returns from reserve assets in a high-interest-rate environment [1][3][7] - The company is in talks for a financing round that could value it at $500 billion, potentially making it one of the most valuable private companies globally [1][6][8] - Tether's USDT market capitalization accounts for approximately 60% of the stablecoin market, with over 500 million users, reflecting its expanding global footprint [1][4][9] Financial Performance - Tether's unique business model supports its high profitability, with a reserve asset portfolio primarily consisting of cash and short-term U.S. Treasury securities, generating significant interest income [7] - The company reported a profit of about $13 billion last year, benefiting from the high-interest environment [7] - Tether's USDT currently has a circulating value of approximately $183 billion, representing a dominant market share [7] Financing and Valuation - Tether is negotiating to raise up to $20 billion by selling about 3% of its shares, which would elevate its valuation to around $500 billion, surpassing companies like ByteDance and matching OpenAI [6][8] - The company has received significant interest from major investors, including SoftBank and Ark Investment Management, indicating strong external confidence in Tether's business model [8] User Base and Market Expansion - Tether's user base has surpassed 500 million, equating to about 6.25% of the global population, showcasing its extensive reach [4][9] - The company plans to re-enter the U.S. market later this year with a new stablecoin project named USAT, aiming to leverage favorable regulatory conditions [9] - Tether is diversifying its investment portfolio, including a notable investment in Juventus Football Club, where it holds 11.5% of shares and is seeking to influence the board [9]
今年利润预计150亿美元,利润率高达99%,用户数超5亿,估值5000亿美元!“稳定币老大”Tether“春风得意”
Hua Er Jie Jian Wen· 2025-10-25 01:48
Core Insights - Tether Holdings Ltd. is attracting global capital due to its impressive profitability and market dominance, with an expected profit nearing $15 billion this year and potential financing discussions that could value the company at $500 billion [1][3][5] Financial Performance - Tether's profit margin is an astonishing 99%, driven by high-interest income from its substantial reserve assets, primarily consisting of cash and short-term U.S. Treasury securities [5][6] - The company reported a profit of approximately $13 billion last year, benefiting from the high-interest rate environment [5][6] Market Position and User Base - Tether's USDT currently has a market circulation value of about $183 billion, holding approximately 60% of the entire stablecoin market [5] - The number of "real users" of Tether has surpassed 500 million, representing about 6.25% of the global population, indicating its extensive global influence [1][7] Financing and Valuation - Tether is in negotiations to raise up to $20 billion by selling about 3% of its shares, which could elevate its valuation to around $500 billion, placing it among the world's top unicorn companies [3][6] - Major investment firms, including SoftBank and Ark Investment Management, have shown interest in participating in this financing round, which could enhance Tether's mainstream applications in technology and finance [6][7] Business Expansion - Tether plans to re-enter the U.S. market later this year with a new stablecoin project named USAT, aiming to leverage favorable policies towards cryptocurrencies [7] - The company is diversifying its investment portfolio, including a notable investment in Juventus Football Club, where it holds 11.5% of the shares and has proposed two board candidates to represent fans [7]
一起破产把黑石、KKR股价都干崩了
投中网· 2025-10-20 06:45
Core Viewpoint - The bankruptcy of First Brands has triggered a significant decline in the stock prices of major private equity (PE) firms, despite the overall stability of the U.S. stock market, indicating a deep-rooted concern about the financial health of the private credit market and its potential systemic risks [2][3][19]. Group 1: Impact of First Brands Bankruptcy - First Brands filed for bankruptcy on September 28, with liabilities estimated between $10 billion and $50 billion and assets between $1 billion and $10 billion [18]. - The bankruptcy has affected numerous lenders, including traditional financial institutions and private credit funds, leading to concerns about broader implications for the financial system [18][19]. - The incident has raised fears that First Brands' collapse could be the first in a series of failures, potentially leading to a wider financial crisis, reminiscent of the subprime mortgage crisis [18][19]. Group 2: First Brands Company Overview - First Brands was a rapidly expanding automotive parts manufacturer, focusing on the aftermarket with a wide range of products [4][8]. - The company was founded in 2013 and grew through aggressive acquisitions, becoming a major player in the automotive aftermarket by 2024, with net sales reaching $5 billion [8][10]. - The company employed a "paired acquisition" strategy, acquiring brands with strong market presence and those with local manufacturing capabilities to enhance production efficiency [7][10]. Group 3: Financial Practices and Risks - First Brands' expansion was heavily financed through unconventional means, including private credit and complex off-balance-sheet financing, leading to a significant accumulation of hidden debt [11][12]. - The lack of regulatory oversight allowed First Brands to avoid disclosing the full extent of its off-balance-sheet liabilities, creating a misleading picture of its financial health [11][12]. - The company's financial troubles became apparent when it attempted to refinance $6.2 billion in debt, leading to a collapse in bond prices and a downgrade to junk status by rating agencies [12][13]. Group 4: Broader Industry Implications - The rapid growth of the private credit market, which has expanded tenfold over the past decade, has created a new "shadow banking" system, raising concerns about the quality of assets held by investors [19]. - Major PE firms, despite not being directly linked to First Brands, have seen their stock prices decline due to fears surrounding their own private credit operations, which have become crucial revenue sources [19].